Doctors Zone
Journal (JEBH)
Alpha™- Liv Drops
Alpha – Liv Drops Due to high demand from the market, for a formulation in drops for the liver, apart from the syrup already available in the market, Schwabe India developed this product. Introduction The liver plays a key role in metabolism. It has anabolic and catabolic, exocrine and endocrine functions. The liver is a blood reservoir, filter and store of different substances (e.g. glycogen, vitamins). It is the site of serum protein (e.g. albumin, prothrombin, fibrinogen) and enzyme synthesis. Metabolic processes (e.g. bilirubin, hormone, carbohydrate and lipid turnover) and the removal of toxic products are important liver functions. 1 Hepatotoxins (e.g. alcohol, tetracycline, acetaminophen, fungal toxins, and anabolic steroids) can cause specific damage to liver cells. Toxic hepatitis may be clinically silent or severe enough to lead to the rapid development of hepatic failure. Clinical features include hepatomegaly, enzyme abnormalities, fever, abdominal pain, anorexia, nausea, vomiting and weight loss. In patients with underlying cirrhosis, manifestations of portal hypertension may predominate. Aversion to fatty food, abdominal discomfort, nausea and vomiting after meals may be symptoms of 2 cholelithiasis. Jaundice results from accumulation of bilirubin. It has non-hepatic as well as hepatic causes. Hyperbilirubinaemia may be due to abnormalities in the 3 formation, transport, metabolism or excretion of bilirubin. TM Alpha -Liv Drops aids recovery and normalisation of liver functions. Severe liver disease needs specialised treatment. Indications: Slow liver functions, fatty liver, and for supportive treatment of hepatocellular jaundice and toxic liver damage.

Schwabe News Octuber to December 2016 Euphorbia lathyris
Euphorbia lathyris
It is commonly known as Caper Spurge. Euphorbia lathyris is an ornamental biennial plant with upright unbranched stems which carry four rows of rigidly arranged deep green leaves. It is fast growing and can grow up to 120cm tall. As a biennial, it will send up stems of leaves in its first year and flower in its second year. The flowers themselves tend to be inconspicuous and are yellow-green in colour. The seeds grow in green clusters of three seeds. When they ripen, they dry out and turn brown, looking a little like Capers, they give them their common name of the Caper Spurge. It will readily self-seed, so the flowers are often removed as they fade to prevent the garden becoming a forest of its seedlings.
Leaves contain quercetin, quercetin-3-b-D-glucuronide, kaempferol, kaempferol 3- glucuronide, b-sitosterol, p-coumaric acid, and ferulic acid. Stalks contain hentriacontane, taraxerone, taraxerol, b-sitosterol, and betulin. The energy-promising latex contains 0.5% 3, 4-dioxyphenylalanine. Sachs et al. (1981) got 6.2% rosin content (hydrocarbons) in non-irrigated, compared to 4.4% on irrigated plots.
It is native of Europe; introduced and naturalized in eastern United States from southern New England to Ohio, south to North Carolina, and in California, having spread from cultivation to roadsides, waste places etc.
A homoeopathic mother tincture is prepared from the whole plant. It is covered by Homoeopathic Pharmacopoeia of United States.
It is useful in dropsy, oedema, tumours, amenorrhoea, schistosomiasis, scabies and snake bites. According to a report it is also useful in leukaemia. In northern America this drug is used to cause abortion. Dr. W. Boericke indicates its use in erysipelas. It also has therapeutic value in paralytic weakness of knee joints. It is reported that it removes corns. It is being used as depilatory (a substance used to remove unwanted hair).
Recommended dose: Q/1x 5 drops. 3rd to 30th potency
Caution: Do not consume during pregnancy.
References:
- P. N. Varma, Indu Vaid, Encyclopaedia of Homoeopathic Pharmacopoeia, Updated edition 2007, B. Jain Publishers, New Delhi.
- Andrew Chevallier, The Encyclopedia of Medicinal Plants, 1st Edition, 1996, Dorling Kindersley, London.
- http://www.seedaholic.com/euphorbia-lathyris.html
- Purdue University, Source: James A. Duke. 1983. Handbook of Energy Crops, source https://www.hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/duke_energy/Euphorbia_lathyris.html
- Chopra. R. N., Nayar. S. L. and Chopra. I. C. Glossary of Indian Medicinal Plants (Including the Supplement) New Delhi: Council of Scientific and Industrial Research. 3rd reprint, 1992. Vol. 2
- Yeung. Him-Che. Handbook of Chinese Herbs and Formulas, Publisher- Institute of Chinese Medicine, 1995
- Coffey. T. The History and Folklore of North American Wild Flowers, Publisher- Facts on File, 1993
Recent Advancements in Basic Homeopathic Research – A Report on Two Significant Publication
In a study conducted at the Experimental Farm of the State University of Santa Catarina, Brazil, researchers investigated the impact of homeopathic treatments on piglets during the nursery phase. The study aimed to determine whether homeopathic agents could reduce fighting behavior, improve growth performance, and affect hematological, metabolic, and oxidative variables. The study included 108 weaned piglets divided into four groups: a negative control group receiving only the basal diet, and three groups receiving different homeopathic treatments at varying dosages.
Journal of Evidence Based Homeopathy Volume: 1, Issue: 1, January - June 2023
Comprehensive articles

Agrohomeopathy – A Review
Short cases

Unmasking the Intricacies: A Pyogenic Abscess Case Report

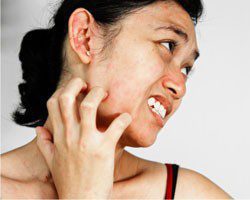
Lichen Simplex: A Singular Case Study

Ranula Unveiled: A Case Report and Management Approach

Lichen Simplex: A Singular Case Study

A Puzzling Presentation: A Case Report of Jaundice
Recent provings and updated materia medica

Acidum Formicum

Mygale

Thea Chinensis
Materia medica on phytohomeopathy

Chrysarobinum

Sanguinarinum nitricum

Thiosinaminum
Mother tincture

Asparagus Officinalis

Ginkgo Biloba

Rosmarinus Officinalis
Product watch

Alpha™- Liv Drops

Good Morning™ Constipation Drops

Zauber™ Hair Drops
Research News