Doctors Zone
Journal (JEBH)
Alpha™- Liv Drops
Alpha – Liv Drops Due to high demand from the market, for a formulation in drops for the liver, apart from the syrup already available in the market, Schwabe India developed this product. Introduction The liver plays a key role in metabolism. It has anabolic and catabolic, exocrine and endocrine functions. The liver is a blood reservoir, filter and store of different substances (e.g. glycogen, vitamins). It is the site of serum protein (e.g. albumin, prothrombin, fibrinogen) and enzyme synthesis. Metabolic processes (e.g. bilirubin, hormone, carbohydrate and lipid turnover) and the removal of toxic products are important liver functions. 1 Hepatotoxins (e.g. alcohol, tetracycline, acetaminophen, fungal toxins, and anabolic steroids) can cause specific damage to liver cells. Toxic hepatitis may be clinically silent or severe enough to lead to the rapid development of hepatic failure. Clinical features include hepatomegaly, enzyme abnormalities, fever, abdominal pain, anorexia, nausea, vomiting and weight loss. In patients with underlying cirrhosis, manifestations of portal hypertension may predominate. Aversion to fatty food, abdominal discomfort, nausea and vomiting after meals may be symptoms of 2 cholelithiasis. Jaundice results from accumulation of bilirubin. It has non-hepatic as well as hepatic causes. Hyperbilirubinaemia may be due to abnormalities in the 3 formation, transport, metabolism or excretion of bilirubin. TM Alpha -Liv Drops aids recovery and normalisation of liver functions. Severe liver disease needs specialised treatment. Indications: Slow liver functions, fatty liver, and for supportive treatment of hepatocellular jaundice and toxic liver damage.

Janosia ashoka – Used for Arnemorrhoea, Menorrhagia – Schwabe India
Schwabe News Volume 3 | Issue 5 & 6| October & December 2012
Janosia ashoka
It is also known by the name Janosia asoca or Saraca indica. It is of the family Leguminosae and is an Indian tree 7-10 m. high with glabrous branches, 15-20 cm long glabrous leaves with 4-6 pairs of leaflets. The tincture is made from the bark and is a proved medicine (1). The affinity of this drug is female reproductive organs. The mother tincture is generally used for delayed and irregular menses, menstrual colic, arnemorrhoea, pain in ovaries before flow, menorrhagia, irritable bladder with other symptoms like unilateral headache, reflex uterine, congestive headache, better open air and by free flow. Desire for sweets, also acid things, thirsty, excessive nausea, obstinate constipation, haemorrhoids are also covered (2,3).
It has many phytochemicals which have been extensively worked pharmacologically and clinically. Ketosterol, a glycosidal fraction, a saponin and an organic calcium compound are found from the whole plant. Ketosterol and the calcium salts are important in the treatment of menorrhagia (4,5). 11-Deoxyprocyanidin B-isolated from root bark (-) epicatechin and procyanidin B2 and other phytochemical have also been isolated. A phenolic glycoside showed highly potent and specific oxytocic activity in vitro and in vivo on uteri of rat and isolated human myometrial strips and fallopian tube. It was active in remarkably low concentrations and nontoxic to animals upto 250 mg/kg (6). Two crude glycosides isolated from bark have exhibited uterine spasmogenic activity and both showed significant stimulant action on isolated uteri of rat, guinea pig, rabbit, dog and human; pure phenolic glycoside P2 was highly potent and showed consistent oxytocic activity (7).
Recommended dose: The recommended Janosia Ashoka uses are10-20 drops 2-3 times a day, depending upon the case
References:
- P. N. Varma, Indu Vaid, Encyclopaedia of Homoeopathic Pharmacopoeia, Updated edition 2007, B. Jain Publishers, New Delhi.
- S. C. Ghose, Drugs of Hindoosthan, With their Homoeopathic Uses, Provings and Clinical Verifications, Hahnemann Publishing Company Pvt.ltd, 165 Bipin Behary Ganguly Street, Calcutta-700 012, Ninth Edition, Reprint Dec. 1998
- W. Boericke, New Manual of Homoeopathic Materia Medica & Repertory [with Relationship of Remedies], Second Re-Augmented & Revised Edition Based on Ninth Edition, Reprint Edition 2002, B. Jain Publishers, New Delhi.
- Sen, S. P., Chemical study of the Indigenous plant Saraca Indica (Asoka), Current Sec. 1963, 32, 502
- Indian J. Pharm. 1964, 26, 110
- D N Prasad, G V Satyavati, P K Das, S P Sen, Oxytocic Activity Of A Pure Phenolic Glycoside (P2) From Abaca Indica Linn (Ashoka) : A Short Communication, Indian J. Med. Res. 1970,58, 660
- G V Satyavati, D N Prasad, S P Sen, P K Das, Further Studies On The Uterine Activity Of Saraca Indica Linn, Indian J. Med. Res. 1970, 58, 947
Recent Advancements in Basic Homeopathic Research – A Report on Two Significant Publication
In a study conducted at the Experimental Farm of the State University of Santa Catarina, Brazil, researchers investigated the impact of homeopathic treatments on piglets during the nursery phase. The study aimed to determine whether homeopathic agents could reduce fighting behavior, improve growth performance, and affect hematological, metabolic, and oxidative variables. The study included 108 weaned piglets divided into four groups: a negative control group receiving only the basal diet, and three groups receiving different homeopathic treatments at varying dosages.
Journal of Evidence Based Homeopathy Volume: 1, Issue: 1, January - June 2023
Comprehensive articles

Agrohomeopathy – A Review
Short cases

Unmasking the Intricacies: A Pyogenic Abscess Case Report

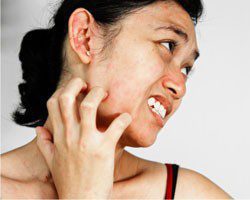
Lichen Simplex: A Singular Case Study

Ranula Unveiled: A Case Report and Management Approach

Lichen Simplex: A Singular Case Study

A Puzzling Presentation: A Case Report of Jaundice
Recent provings and updated materia medica

Acidum Formicum

Mygale

Thea Chinensis
Materia medica on phytohomeopathy

Chrysarobinum

Sanguinarinum nitricum

Thiosinaminum
Mother tincture

Asparagus Officinalis

Ginkgo Biloba

Rosmarinus Officinalis
Product watch

Alpha™- Liv Drops

Good Morning™ Constipation Drops

Zauber™ Hair Drops
Research News