5 Lifestyle Changes To Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
- Dr. Aditi Sharma
- No Comments

Diabetes or diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disease characterized by elevated glucose levels in the blood. It is associated with impairment in the body’s ability to process blood sugar. This happens either due to inadequate production of insulin hormone by the pancreas, known as Type-1 diabetes, or resistance of the body’s cells to insulin (insulin resistance), also called Type-2 diabetes. Diabetes has been found to be a lifestyle-related disorder. This article will shed light on diabetes prevention strategies for health and wellness.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Diabetes?
Signs and symptoms of diabetes are: –
- Polydipsia or increased thirst.
- Polyuria or frequent urination.
- Causeless fatigue or feeling tired unusually.
- Blurred vision
- Unexplained loss of weight
- Frequent infections or slow-healing wounds
- Tingling or numbness in hands or feet
- Polyphagia or increased hunger
Also Read Top 5 Lifestyle Habits that can Manage your Diabetes
What Are The Causes Of Diabetes?
The causes and risk factors of Type 1 diabetes are: –
- Autoimmune reaction that damages the beta cells in the pancreas.
- Positive family history
- Certain viral infections
The causes and risk factors of Type 2 Diabetes are: –
- Positive family history.
- Obesity, especially excess belly fat.
- Physical inactivity
- An unhealthy diet is high in sugar, unhealthy fat, and processed food.
- Age- Increasing age, especially after 45 years of age.
- Ethnicity- African, Native American, Hispanic, and Asian individuals are at higher risk.
- High blood pressure and high cholesterol
- Women who have had gestational diabetes.
- Chronic stress and stress hormones
- Sleep disturbances such as sleep apnoea
- Certain medications, such as steroids or certain antipsychotic drugs
What Are The Complications Of Diabetes?
The complications associated with diabetes are: –
- Cardiovascular diseases such as heart disease and stroke.
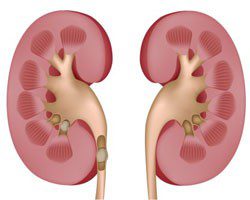
- Diabetic nephropathy
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Diabetic retinopathy and other eye problems such as glaucoma and cataracts.
- Foot problems in which even minor foot injuries can lead to ulcers and infections that may even require amputation.
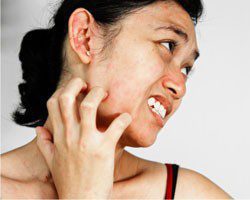
- Diabetic dermopathy causes dry, itchy, and scaly patches on the skin. Also, people with diabetes are more prone to bacterial and fungal skin infections.
- Periodontal problems
- Hearing impairment
- Cognitive decline
- Increased risk of particularly respiratory and urinary tract infection.
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
Also Read Diabetes And Weight Loss: Myths Vs. Facts
What Are The Lifestyle Changes For Type 2 Diabetes Prevention?
Healthier lifestyle choices for diabetes risk reduction are: –
1. A healthy diet and healthy eating habits.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in lean protein, healthy unsaturated fats such as nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil, and complex carbohydrates or fibre such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. A reduction in sugar intake, such as that found in sugary drinks and sweets, is needed for blood sugar control.
- Practice portion control, as eating large portions of even healthy foods can lead to weight gain. Instead, try eating smaller and more frequent meals.
- Practice mindful eating- This includes thoroughly chewing the food, savoring the food, avoiding TV mobile while eating, and being attentive to the body’s cues regarding when one is hungry and when one is full.
- Stay hydrated and drink plenty of water.
- Quit smoking
- Limit intake of alcohol- For women, the limit is up to one drink a day, and for men, it is up to two drinks in a day. Also, opt for healthier options such as light beer, dry wine, or spirits without sugary mixers.
2. Regular physical activity for physical fitness.
- Follow an exercise routine- Include at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity every week, e.g., swimming, cycling, or walking, or 75 minutes of high-intensity exercise per week, e.g., running in routine.
- Do strength training- Do resistance exercises, e.g., weight-lifting or resistance bands, for at least two days a week.
- Avoid sedentary behavior- Apart from routine workouts, take the stairs, use a standing desk, cycle, or walk for short trips.
3. Weight Management
- Maintain a healthy weight – Losing even 5-10% of body weight can be helpful to reduce the risk.
- Aim for gradual weight loss of 1-2 pounds per week and avoid crash dieting.
- Monitor waist circumference -: Aim to keep waist measurement under 35 inches for women and 40 inches for men.
4. Practice stress management
- Get enough sleep of up to 7-9 hours each night. Follow a sleep routine and try to go to bed and wake up at the same time each night. Also, avoid coffee, TV, or mobile phones around bedtime.
- Improve sleep quality – In cases of conditions like sleep apnea that adversely affect sleep quality, refer to a healthcare provider.
- Practice mind-relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises, and regularly spend some time in nature to manage chronic stress.
- Engage in fun activities or spend some time with family and friends to relax and reduce stress levels.
5. Regular monitoring
- Know your numbers – Get blood pressure, blood glucose levels, and cholesterol levels checked regularly. This is especially important if there is a risk of getting diabetes due to the presence of factors such as being overweight, having hypertension, or positive family history of diabetes.
Also Read Homeopathic Medicine for Diabetes
Conclusion
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disease characterized by elevated glucose levels in the blood. Signs and symptoms associated with diabetes are polydipsia, polyuria, polyphagia, causeless fatigue, and weight loss. Factors causing type 1 diabetes are autoimmunity, positive family history, and certain viruses. Causes of type 2 diabetes are positive family history, obesity, unhealthy diet, sedentary life, chronic stress, sleep disturbances, prediabetes, and gestational diabetes. If not treated in a timely manner, diabetes can lead to several complications such as diabetic neuropathy, nephropathy, dermopathy, retinopathy, and increased tendency for urinary tract and respiratory infections. As prevention is better than cure, important diabetes prevention tips include nutritional awareness for diabetes and mindful eating, chronic stress management, weight management, sleep management, and regular monitoring of important parameters like blood glucose, blood cholesterol, and blood pressure, especially if one has one or more risk factors for diabetes such as positive family history, excess belly fat or hypertension.